Deceptive Browser Extensions within the Google Store: A Study in AI Slop
Like any garden, the digital landscape experiences the emergence of unexpected blooms. Among the helpful flora of browser and application extensions, some appear with intentions less than pure. These deceptive ones, often born from a fleeting desire for illicit gain or mischievous disruption, may possess a certain transient beauty in their ingenuity. They arrive, sometimes subtly flawed in their execution, yet are driven by an aspiration to infiltrate our digital lives, to harvest our data, or to simply sow chaos.
We see them not in complete, monolithic forms, but in their evolving iterations. A small crack in their initial design might be patched in the next update, a vulnerability exploited and then hastily concealed. Their existence is a dance of adaptation, a response to the ever-watchful gaze of security systems. They are, in a sense, perfectly imperfect – their flaws often intertwined with the very mechanisms that allow them to function, however briefly.
On the other side of this digital ecosystem reside the forces of security and risk awareness. These are the gardeners, constantly tending to the health of the digital space, pruning away the harmful growths. Security measures, with their own imperfections and constant striving for improvement, represent the human desire for safety and control. Risk, then, is the shadow cast by these deceptive extensions, a reminder of the potential cost of their transient existence – the loss of privacy, the compromise of personal information, the erosion of trust in the digital tools we rely upon.
The human experience at the heart of this is one of vulnerability and resilience. We, the users, navigate this landscape, often unaware of the subtle battles being waged. We place our trust in the extensions we install, hoping for enhanced functionality or convenience. When that trust is betrayed by a deceptive app or extension, it leaves a mark, a subtle crack in our digital confidence.
This story is a reminder that the digital world, like the natural one, is in constant flux, and our experience within it is shaped by this delicate and ever-shifting balance between aspiration and risk, between the fleeting beauty of innovation and the enduring need for security.
Browser Extensions’ Security Risk
Browser extensions can pose a security risk to individuals and organizations. Data from the user’s browser or inputs to the extensions can be sent to third parties who may not practice effective security measures to protect user data and privacy. This report highlights a network of approximately 20 newly registered websites intended to lure people to install new browser extensions from the Google Store. The domains and extensions were likely created by a single author, which exhibit patterns of deceptive practices and potential security risks. While the extensions do not display overtly malicious behavior, their design choices raise concerns regarding user privacy and data security.
The Network and Its Characteristics:
The extensions, available on the Google Chrome Web Store, share several common traits:
Manipulated Ratings: All extensions employ a deceptive rating system, funneling positive reviews to the Chrome Web Store while discarding negative feedback.
External Data Transmission: Some extensions, particularly those offering AI-powered features, transmit user data to domains owned by the author. This includes chat history, input data, and potentially sensitive information.
Misleading Branding: Certain extensions use misleading branding, falsely associating themselves with well-known services (e.g., “DeepSeek AI”).
Functional Diversity: The extensions offer a range of functionalities, including AI writing and ad creation tools, URL shortening, PDF to JPG conversion, and AI chatbots.
Security Researcher’s Guide: Investigating Suspicious Browser Extensions:
Investigative Steps:
- Initial Observation:
- Note the extension’s stated functionality and its perceived utility.
- Examine user reviews for consistency and authenticity. Be wary of overwhelmingly positive reviews with limited negative feedback.
- Record the developer’s name and any associated websites or domains.
- Extension Retrieval:
- Obtain the Extension ID: Locate the extension on the Chrome Web Store or via a URL from a website directing to download the extension
- Download the Extension: Use a tool like chrome-stats[.]com to download the extension’s .crx file.
- Unpack the Extension: One method is to use a file archiving tool (e.g., 7-Zip) to extract the contents of the .crx file.
- Analyze the Files:
- Examine the manifest.json file for permissions requests and service worker details. Pay attention to permissions that seem excessive for the extension’s stated functionality.
- Analyze Javascript files for suspicious code, external API calls, and data transmission patterns. Look for obfuscated or unusual code that may warrant further investigation.
- Review the Domains: Research the domains that the extension uses, and be suspicious of generic or unknown domains. Assess the domain’s registration information, hosting provider, and overall reputation.
- Data Flow Assessment:
- Identify the types of data being transmitted and the purpose of the transmission. Evaluate the security and privacy implications of the data transmission.
Examples:

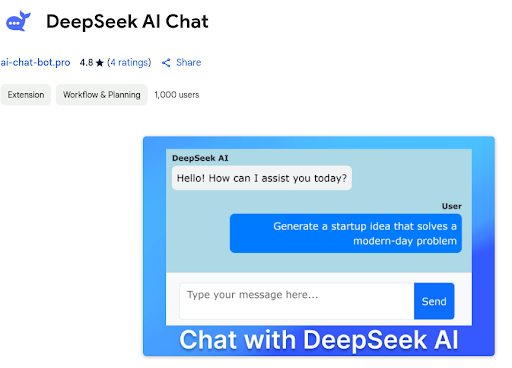
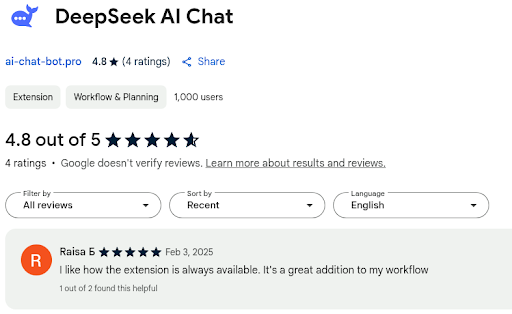
An interested user might see the reviews are 4.8 stars and at least 1,000 users. Not an insubstantial number given the recent global proliferation of DeepSeek AI related apps in the past few months.
A closer look at the reviews shows 4 ratings.
Domain | ai-chat-bot[.]pro |
| Google Store URL | https[:]//chromewebstore.google[.]com/detail/deepseek-ai-chat/jmpcodajbcpgkebjipbmjdoboehfiddd |
Extension ID | jmpcodajbcpgkebjipbmjdoboehfiddd |
Filename | jmpcodajbcpgkebjipbmjdoboehfiddd.crx |
Sha256 | aa6901e5a6dcfae8cca4b06278fd3ed2e429e8ec29bb3ca39e0dd1cd428320e2 |
The extension’s core functionality involves capturing user input and the entire ongoing chat history, then transmitting this data to an external server (ai-chat-bot.pro) with every message sent by the user. This presents a significant privacy risk, as potentially sensitive conversation data is processed by an unverified third party.
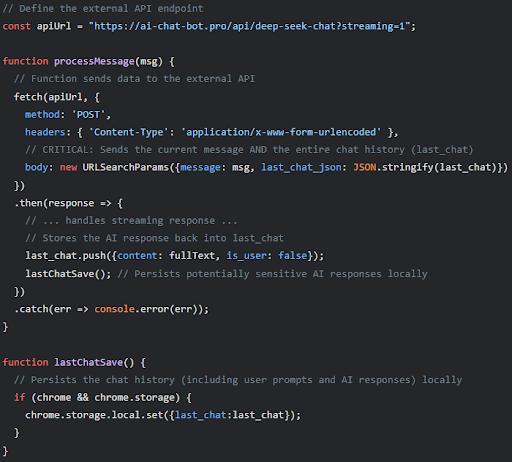
Common among all the observed extensions by this author is code that includes a rating widget that actively filters user feedback. Users providing low ratings (1-3 stars) are redirected to a private feedback form on the ai-chat-bot[.]pro domain, while users providing high ratings (4-5 stars) are sent to the official Chrome Web Store (CWS) review page. This artificially inflates the extension’s public rating and violates CWS policy.
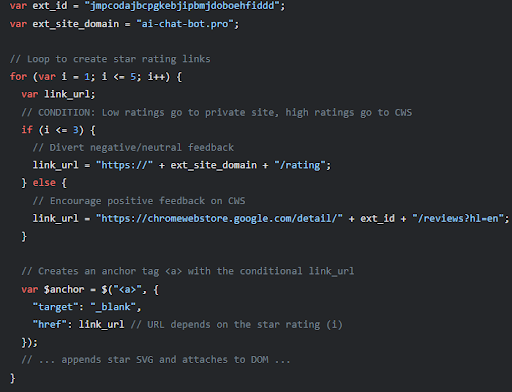
A background script directs users to pages hosted on the same suspicious ai-chat-bot[.]pro domain upon extension installation (welcome page) and sets it as the target URL upon uninstallation. This allows the external server to track install/uninstall events.
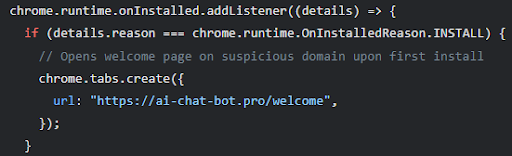
The code opens a new tab that loads the following page:
This page then sets multiple Yandex tracking cookies without permissions and retrieves browser information from the user.
Even without overtly malicious intent, the observed review manipulation and external transmission of the user’s IP, browser information and associated chat history raise concerns. This grants the website owner access to sensitive user interactions, a potentially serious issue given the increasing data leakage associated with AI productivity tools. The rapid adoption of AI integrations, facilitated by accessible browser extensions, can lead to a gradual erosion of security practices as users develop a false sense of trust. This “out of sight, out of mind” mentality risks exposing sensitive data, such as code, personal searches, and AI chatbot inputs, to malicious third parties who may engage in eavesdropping, data selling, or exploitation.
Looking For More: Domain Registration Patterns
- IP Resolved: 164.90.199[.]205
- IP ISP: DigitalOcean LLC
- Use Yandex Trackers: 99419511 / 99794673 / 99764413
- Registrar: Porkbun LLC
- SSL Issuer: R10 / R11
- NameServer Domain: messagingengine[.]com
- Server Type: Apache/2.4.52 (Ubuntu)
- MX Domain: messagingengine[.]com
| Domain: ai-sentence-rewriter[.]com Extension Name: ai-sentence-rewriter Extension ID: ihdnbohcfnegemgomjcpckmpnkdgopon | |
| pdf-to-jpg[.]app Extension Name: convert-pdf-to-jpg Extension ID: oeefjlikahigmlnplgijgeeecbpemhip | |
| Domain: htmlvalidator[.]app Extension Name: html-validator Extension ID: aofddmgnidinflambjlfkpboeamdldbd | |
| Domain: email-checker[.]pro Extension Name: email-checker-verify-emai Extension ID: eheagnmidghfknkcaehacggccfiidhik | |
| Domain: u99[.]pro Extension Name: link-shortener Extension ID: oliiideaalkijolilhhaibhbjfhbdcnm |
AI Slop
“AI Slop” refers to low-quality, often generic and repetitive content, including text and images, generated by artificial intelligence, indicating a lack of human oversight and effort. In this case, the presence of many uniformly structured websites, each with minimal, repetitive content and duplicated code across their associated browser extensions, may suggest it is the product of AI Slop. The generic stock imagery, boilerplate text, and superficial explanations of extension functionality, align with the definition, indicating a potential reliance on automated AI generation rather than thoughtful development.
A Surge in AI Slop
Continuing our exploration of the digital landscape, we now see a new element stirring the garden: a surge of growth we might call “AI Slop.” This refers to the rapidly increasing volume of apps and extensions, often born with the assistance of artificial intelligence, that flood the digital stores without the careful cultivation of thoughtful development, particularly around ethical considerations, privacy and security.
This influx amplifies the transient nature of the deceptive Chrome extensions we’ve discussed. AI tools can accelerate their creation and deployment, leading to a more rapid cycle of appearance, exploitation, and eventual detection. The digital garden becomes overgrown, making it harder to discern the true blooms from the weeds.
Deceptions and user risks over privacy and security we observe in hand-crafted malicious extensions can be magnified in those influenced by AI Slop. While AI can generate code quickly, it might lack the nuanced understanding of security vulnerabilities or the ethical considerations that human developers often bring. This can result in extensions riddled with unintentional flaws that are nonetheless exploitable, or even intentionally deceptive features woven into the code with algorithmic efficiency.
The “aspirations” of these AI-assisted deceptive extensions might be less about ingenious design and more about sheer volume. The ease with which they can be generated lowers the barrier for malicious actors, potentially leading to a flood of mediocre but still harmful extensions aimed at overwhelming users and security systems alike. The digital storefronts become crowded marketplaces where discerning genuine value from deceptive imitation becomes an increasingly difficult task for the average user.
The human experience is significantly impacted by this AI Slop. Users, already faced with a bewildering array of choices, are now confronted with an even greater volume of extensions and apps, many of them indistinguishable from legitimate options at a glance. The ability to pick the “perfect” extension becomes an exercise in futility, as the sheer quantity dilutes the quality and increases the risk of encountering a deceptive one. This overabundance erodes trust not just in individual extensions and apps, but in the platforms themselves.
The forces of security now face an even greater challenge. The volume and rapid evolution of AI-Slop-driven extensions and apps make detection and mitigation a constant uphill battle. Traditional signature-based approaches struggle to keep pace with the algorithmic generation of new threats. The gardeners of the digital space must now adapt to a landscape where weeds can sprout with unprecedented speed and in overwhelming numbers.
IOCs on GitHub
https://github.com/DomainTools/SecuritySnacks/blob/main/2025/DeceptiveBrowserExtensions-AISlop
If the community has any additional input, please let us know.
Sign Up For DomainTools Investigations’ Newsletter for the Latest Research
Want more from DomainTools Investigations? Be sure to sign up for our monthly newsletter to get the latest research from the team – available on LinkedIn or email.